Carbon fiber-reinforced polymer matrix composites are widely used in aerospace, medical, automotive, and shipbuilding industries due to their advantages such as low density, high stiffness, superior strength, and heat resistance.
Twin-screw extrusion technology stands out as the primary method for preparing carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites, owing to its excellent mixing performance, self-cleaning capability, high output, and low energy consumption. Additionally, as injection molding and compression molding techniques become more advanced, the melt produced by twin-screw extrusion can be molded into different shapes according to specific operational requirements.
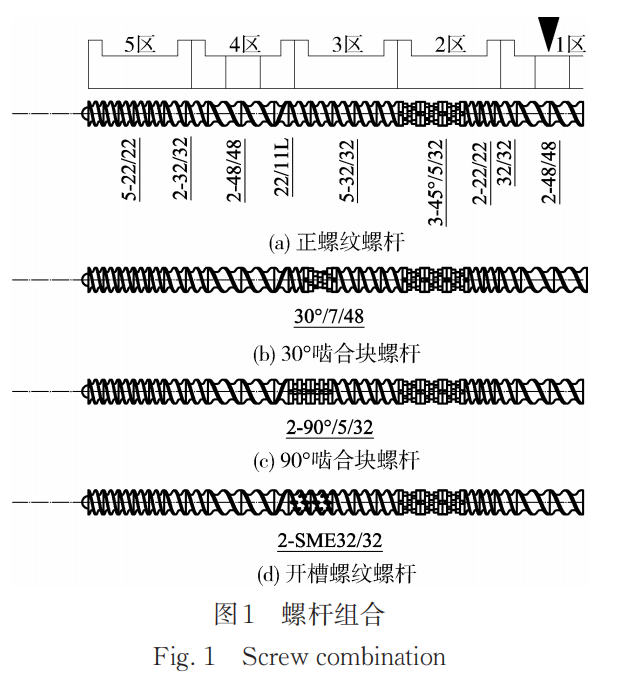
The following four different screw configurations were studied by comparing the residence time of the material in the extruder, fiber distribution, and fiber length retention. This research investigates the influence of screw design on mixing efficiency and extrusion uniformity, providing valuable guidance for the twin-screw extrusion process and practical applications of carbon fiber-reinforced polymer composites.